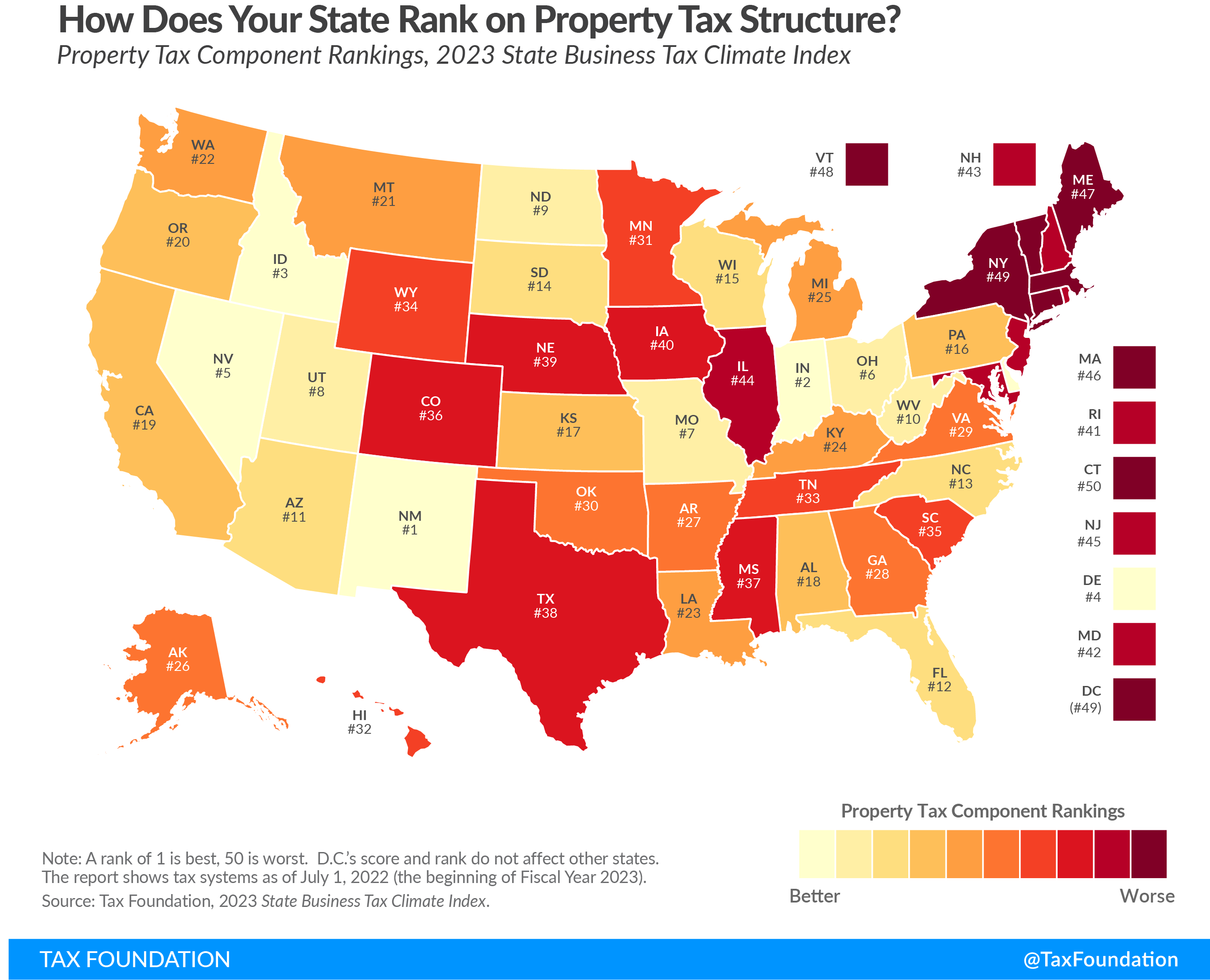
Today’s map shows states’ rankings on the property taxA property tax is primarily levied on immovable property like land and buildings, as well as on tangible personal property that is movable, like vehicles and equipment. Property taxes are the single largest source of state and local revenue in the U.S. and help fund schools, roads, police, and other services.
component of our 2023 State Business Tax Climate Index. The Index’s property tax component evaluates state and local taxes on real and personal property, net worth, and asset transfers. The property tax component accounts for 15 percent of each state’s overall Index score.
Property taxes matter to businesses for several reasons. First, businesses own a significant amount of real property, and taxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities.
rates on commercial property are often higher than the rates on comparable residential property. Many states and localities also levy taxes not only on the land and buildings a business owns but also on tangible property, such as machinery, equipment, and office furniture, as well as intangible property like patents and trademarks. Across the nation, property taxes impose one of the most substantial state and local tax burdens that businesses face. In fiscal year 2021, taxes on real, personal, and utility property accounted for almost 39 percent of all taxes paid by businesses to state and local governments, according to the Council on State Taxation.
Although taxes on real property tend to be unpopular with the public, a well-structured real property tax generally conforms to the benefit principle (the idea in public finance that taxes paid should relate to benefits received) and is more transparent than most other taxes.
Taxes on intangible property, wealth, and asset transfers, on the other hand, are harmful and distortive. States that levy such taxes—including capital stock taxes; inventory and intangible property taxes; and estate, inheritance, gift, and real estate transfer taxes—are less economically attractive, as they create disincentives for investment and encourage businesses to make choices based on the tax code that they would not make otherwise. Businesses with valuable trademarks may seek to avoid headquartering in states with intangible property taxes, and shipping and distribution networks might be shaped by the presence or absence of inventory taxes.
States are in a better position to attract business investment when they maintain competitive real property tax rates and avoid harmful taxes on tangible personal property, intangible property, wealth, and asset transfers. This year, the states with the best scores on the property tax component are Indiana, New Mexico, Idaho, Delaware, and Nevada. States with the worst scores on this component are Connecticut, New York, Vermont, Maine, Massachusetts, and New Jersey, plus the District of Columbia.
To gauge whether your state’s property tax structure has become more or less competitive in recent years, see the following table. (Methodological changes are backcast to prior years to facilitate comparability.)
| Property Tax Component of the State Business Tax Climate Index (2020–2023) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | 2020 Rank | 2021 Rank | 2022 Rank | 2023 Rank | Change from 2022 to 2023 |
| Alabama | 19 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 2 |
| Alaska | 25 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 0 |
| Arizona | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 0 |
| Arkansas | 27 | 28 | 29 | 27 | 2 |
| California | 15 | 14 | 14 | 19 | -5 |
| Colorado | 33 | 33 | 34 | 36 | -2 |
| Connecticut | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| Delaware | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Florida | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 0 |
| Georgia | 31 | 27 | 27 | 28 | -1 |
| Hawaii | 28 | 30 | 31 | 32 | -1 |
| Idaho | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Illinois | 44 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 1 |
| Indiana | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | -1 |
| Iowa | 38 | 38 | 39 | 40 | -1 |
| Kansas | 18 | 19 | 19 | 17 | 2 |
| Kentucky | 23 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 0 |
| Louisiana | 29 | 26 | 25 | 23 | 2 |
| Maine | 40 | 40 | 41 | 47 | -6 |
| Maryland | 41 | 43 | 43 | 42 | 1 |
| Massachusetts | 45 | 46 | 46 | 46 | 0 |
| Michigan | 26 | 22 | 23 | 25 | -2 |
| Minnesota | 32 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 1 |
| Mississippi | 37 | 37 | 38 | 37 | 1 |
| Missouri | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| Montana | 21 | 20 | 22 | 21 | 1 |
| Nebraska | 39 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 1 |
| Nevada | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| New Hampshire | 46 | 47 | 47 | 43 | 4 |
| New Jersey | 47 | 44 | 44 | 45 | -1 |
| New Mexico | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| New York | 48 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 0 |
| North Carolina | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 0 |
| North Dakota | 7 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 1 |
| Ohio | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| Oklahoma | 30 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 0 |
| Oregon | 20 | 16 | 17 | 20 | -3 |
| Pennsylvania | 16 | 15 | 15 | 16 | -1 |
| Rhode Island | 42 | 42 | 42 | 41 | 1 |
| South Carolina | 35 | 35 | 36 | 35 | 1 |
| South Dakota | 14 | 23 | 18 | 14 | 4 |
| Tennessee | 34 | 34 | 33 | 33 | 0 |
| Texas | 36 | 36 | 37 | 38 | -1 |
| Utah | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 0 |
| Vermont | 49 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 0 |
| Virginia | 24 | 29 | 28 | 29 | -1 |
| Washington | 17 | 18 | 21 | 22 | -1 |
| West Virginia | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | -1 |
| Wisconsin | 22 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 1 |
| Wyoming | 43 | 39 | 35 | 34 | 1 |
| District of Columbia | 48 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 0 |
|
Note: A rank of 1 is best, 50 is worst. All scores are for fiscal years. DC’s score and rank do not affect other states. Source: Tax Foundation. |
|||||
To learn more about how we determined these rankings, read our full methodology.
Stay informed on the tax policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.
Share this article