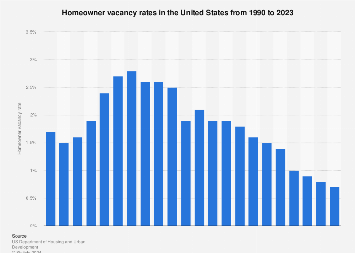
The homeowner vacancy rate in the United States reached its lowest value in 2023. The rate shows what share of owner-occupied housing units were vacant and for sale. That figure peaked in 2008, when nearly three percent of homes were vacant, and gradually fell below one percent after the 2020 housing boom. Homeownership is a form of living arrangement where the owner of the inhabited property, whether apartment, house, or type of real estate, lives on the premises. Due to usually high costs associated with owning a property and perceived advantages or disadvantages associated with such a long-term investment, homeownership rates differ greatly around the world, based on both cultural and economic factors. In Europe, Romania is the country with the highest rate of homeownership, while the lowest homeownership rate was observed in Switzerland.
Homeownership attitude in the U.S.
Individuals may have very different opportunities or inclination to become homeowners based on nationality, age, financial status, social status, occupation, marital status, education or even ethnicity and whether one is local-born or foreign-born. The homeownership rate among older individuals in the United States, for example, is much higher. In the U.S., homeownership is generally believed to be a good investment, in terms of security (no risk of eviction) and financial aspect (owning a valuable real estate property). In 2022, there were approximately 85 million owner-occupied housing units in the United States, a stark increase compared to four decades prior. Despite having your own home being an integral part of the American Dream, across all generations, Americans in a 2022 survey agreed that now is not a good time to buy a home.
Why is homeownership sentiment low?
The housing market has been suffering chronic undersupply, leading to a surge in prices and eroding affordability. In 2022, the housing affordability index plummeted, reflecting the growing challenge that homeowners face when looking for property. Insufficient income, savings, and high home prices ranked as the top obstacles to homebuying for generation Z. Though affordability varied widely across different metros, just about 15 percent of U.S. renters could afford to buy the median priced home in their area.
