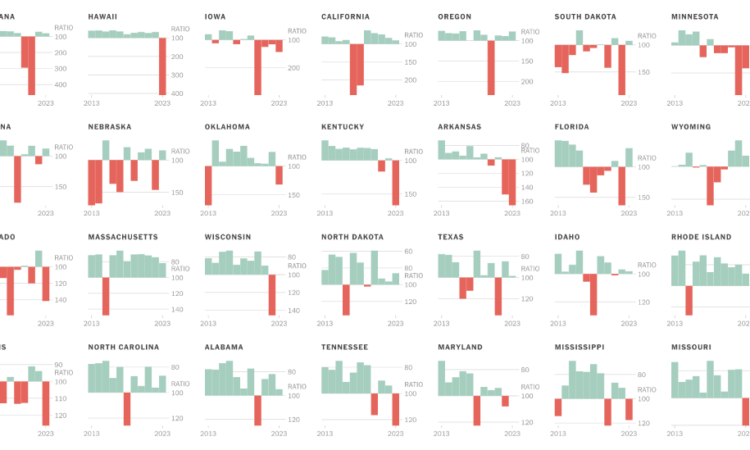
As climate change makes disasters more frequent and severe, the insurance industry is in tumult. Losses have been spreading beyond states that have been ravaged by hurricanes and wildfires, like Florida and California, and into places like Iowa, Arkansas, Ohio, Utah and Washington. Even in the Northeast, where homeowners insurance was still generally profitable last year, trends are worsening.
Find your state:
the homeowners insurance market has been unprofitable for the past four years because of severe storms. Insurers are limiting coverage and some are leaving the state.
Profitability of homeowners insurance in Iowa
Source: AM Best
Ratio of costs to revenue for homeowners insurance statewide.
To measure the financial health of the homeowners insurance industry, The New York Times assembled data that compares revenues with costs for insurers in each state.
The data show that homeowners insurance was unprofitable in 18 states last year, up from eight in 2013. Most of those states are in the interior of the country, hit by severe storms and hail in the Midwest and Southeast, and wildfires in much of the West. In response to those losses, insurers have raised premiums, narrowed coverage and dropped customers, and even entirely withdrawn from some states.
A shaky insurance market threatens the entire economy. Without insurance, banks won’t issue a mortgage; without a mortgage, most people can’t buy a home. With fewer buyers, real estate values are likely to decline, along with property tax revenues, leaving communities with less money for schools, police and other basic services.
Insurers are regulated by states, which are trying different strategies to shore up the industry: Making it easier for companies to raise premiums or encouraging homeowners to make their homes more resilient to damage. It’s not yet clear if any of those strategies are working, especially as Americans keep moving to high-risk areas and as climate change gets worse.
“Insurance is where many people are feeling the economic impacts of climate change first,” said Carolyn Kousky, associate vice president for economics and policy at the Environmental Defense Fund. “That is going to spill over into housing markets, mortgage markets, and local economies.”
See the rest of the country:
Nationally, over the last decade insurers paid out more in claims than they received in premiums, according to the ratings firm Moody’s, and those losses are increasing.
Losses in some states have been worse than in others. In the charts below, each state is on its own scale. To compare all the states on the same scale, click the “shared scale” button.
Home Insurance Profitability in Every State
Methodology
Insurance profitability charts show the direct combined ratios in the homeowners sector, which are calculated by dividing costs from payouts and other expenses by revenue from premiums. Combined ratios data was provided by AM Best, based on regulatory filings from insurance companies. The 2023 figures reflect 98 percent of companies reporting.
Direct combined ratios do not include reinsurance payments. Insurers that run an operating loss can still make money by investing their revenue.
Direct combined ratios usually present unprofitable years as having a ratio greater than 100, and profitable years as having a ratio of less than 100. To make the data easier to interpret, the charts in this article use an inverted Y axis, so that unprofitable years appear as negative values and profitable years as positive values.
Data cited on insured losses do not account for inflation.
