Investing in real estate is a proven wealth-creation strategy. Real estate investments can also help you diversify your portfolio and protect it from stock market volatility. Let’s look at the most popular options for investing in real estate, the pros and cons, and how you can get started.
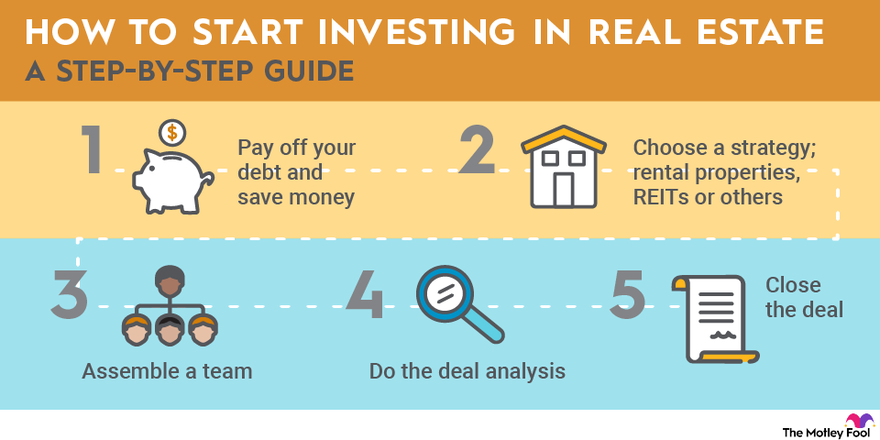
Image source: The Motley Fool.
What are my investment options?
Here are the most popular real estate investment methods:
- Rental properties.
- REITs.
- Real estate investment groups.
- Flipping houses.
- Real estate funds.
Let’s dive deeper into how these work.
Rental properties
Rental properties
Rental properties are among the most hands-on options on this list. You buy a property and rent it to tenants, usually for one or more years. In addition, buying a vacation home and renting it for shorter periods on a platform such as Airbnb (ABNB -6.08%) is becoming more popular.
As the property owner, you are the landlord. You’re responsible for upkeep, cleaning between tenants, repairs, and paying property taxes. Depending on the lease terms, you may be on the hook for replacing appliances and paying for utilities.
You make money off rental properties from the rental income you receive from tenants and price appreciation if you sell the property for more than you paid.
You can also benefit from tax write-offs. Under passive activity loss rules, you can deduct as much as $25,000 of losses from your rental properties from your normal income if your modified adjusted gross income is $100,000 or less. The deduction phases out by $1 for every $2 of modified adjusted gross income above $100,000 until it completely phases out at $150,000. Depreciation (a noncash expense) and interest (which you pay no matter what) can make the property show an accounting loss even when you’re still making money.
When you buy a rental property, you could need a down payment of as much as 25%. In addition, you might incur other startup costs like repairs and renovations. However, you’ll earn income plus any price appreciation.
People with limited available capital could consider a rental arbitrage strategy. You sign a long-term lease on a property of a year or more and rent it on the short-term vacation rental market. You pocket the difference between your expenses (including rent) and the rental income received.
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing money or the premium you get for lending money. Learn how interest rates affect the economy.
REITs
REITs
If you don’t want to put up with the headache of managing a rental property or can’t come up with the down payment, real estate investment trusts (REITs) are an easy way to start investing in real estate.
REITs are companies that own and manage rental properties. They can hold any type of commercial real estate, including medical office space, malls, warehouses, offices, or apartment buildings.
REITs tend to have high dividend payments because they are required to pay out at least 90% of their net income to investors. If the REIT meets this requirement, it will not have to pay corporate taxes.
Additionally, while selling a rental property could take months and mountains of paperwork, a REIT has the advantage of liquidity since many REITs trade on a stock exchange.
Real estate investment groups
Real estate investment groups
Investing in a real estate investment group (REIG) is one way to keep the profit potential of private rental properties while possibly getting more upside than a REIT trading at a premium valuation to the value of its portfolio.
REIGs purchase and manage properties. They sell interests in the property to investors who get a share of the rental income.
The operating company receives a portion of the rent and manages the property. This means the company finds new tenants and takes care of all maintenance. REIGs often will retain some of the rent to pay down debt and meet other obligations if some units are vacant.
Flipping houses
Flipping houses
Flipping houses is the most hands-on, challenging, and risky of these options, but it can be the most profitable. The two most common ways to flip houses are to buy, repair, and sell, or buy, rehab, rent, refinance, and repeat (BRRRR method). In either case, the key is to limit your initial investment with a low down payment and keep renovation costs low.
Let’s say you buy a house for $250,000 with 20% down, or $50,000. You spend another $50,000 on renovations and then sell the house for $400,000. You use the $400,000 to pay off the $200,000 loan and then have $100,000 in profit on a $100,000 investment. It’s a great return if you can get it.
The problem is that you usually can’t. Housing markets can flip from a sellers’ market to a buyers’ market on a dime, which can affect your sales price. Meanwhile, keeping renovation costs to a minimum may sound easy, but it may be nearly impossible if you don’t have direct construction experience. Inflation and delays can push costs through the roof.
If you flip houses, do extensive due diligence. Also, make sure to build in a big cushion in case something doesn’t go according to plan (which is usually the case).
Real estate funds
Real estate funds
Real estate funds invest in REITs and real estate operating companies (REOCs). REOCs are like REITs, but they don’t have to pay dividends, so they grow much faster.
Real estate mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are the simplest ways to invest in real estate. Many have very low minimum investments (for example, Fundrise lets you invest in its real estate funds for only $10, while many REIT ETFs cost less than $100 per share). The fund’s managers pick real estate stocks or property investments that generate income, allowing you to passively collect dividend income.
Even if you’re a stocks-only investor, consider using real estate funds to get diversification while keeping the liquidity profile you’re used to. Investors have many high-quality REIT ETF options.
Should you invest?
Why should you invest in real estate?
Here are a few pros and cons of investing in real estate:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
If you invest in physical property, you can control your investment. You could also have a totally passive investment that you don’t need to manage if you hire a property manager. |
In a Great Recession type of event, prices can collapse and take down your entire portfolio. |
|
Can be a source of steady monthly income payments. |
With the amount of leverage required, even small price drops can wipe out your whole investment. |
|
Can reduce the overall volatility of your investment portfolio through diversification and lower price movements in general. |
If you choose to flip houses or personally own rental properties, it can turn into a career and use up significant free time. |
|
Can lead to long-term wealth creation through the use of leverage. |
Upfront costs can make initial investments difficult. You need to save enough for the down payment and to cover cash flow shortages when there are vacancies. |
How to get started
How to get started in real estate
If you choose to invest directly in real estate through a rental property or fix-and-flip, follow these five steps to get started:
- Save money: Real estate has some of the most expensive barriers to entry of any of the asset classes. Before you get started, you’ll want to pay off your high-interest debt and have significant savings.
- Choose a strategy: Each of the strategies listed above can be successful. If you choose to buy REITs or funds, you can do online research about your options to help you get started. If you want to buy physical property, you’ll need to decide on a market.
- Assemble a team: You may want to work with an agent when you get started. Great agents will send you off-book opportunities that haven’t been listed yet. Eventually, you may need someone to manage your properties and an accountant to handle the financials. If you become successful, you may eventually need investors, too.
- Do deal analysis: Whether you’re investing in residential or commercial real estate, you should do plenty of research on any investment. For example, with rental properties, you’ll need to analyze future rent payments and expenses you may be liable for and forecast your potential sales price.
- Close the deal: The final step is making your first investment. Close on your property, or make the buy in your brokerage account.
Related investing topics
Start investing in real estate today
Real estate investing can seem intimidating at first. Not everyone has the time or ability to flip houses or handle having a tenant. The good news is there are options available for every level of investor, with each catering to different goals, skill levels, and time constraints. That allows anyone to get started today and let the wealth-creation potential of real estate investing begin.
FAQ
FAQ on investing in real estate
Is it worth getting into real estate investing?
Yes, it can be worth getting into real estate investing. Real estate has historically been an excellent long-term investment (REITs have outperformed stocks over the very long term). It provides several benefits, including the potential for income and property appreciation, tax savings, and a hedge against inflation.
Is $5,000 enough to invest in real estate?
Depending on the strategy, $5,000 can be enough to invest in real estate. Many real estate strategies have investment minimums well below $5,000. For example, you can invest in many REITs and REIT ETFs with a few hundred dollars or less. Meanwhile, some real estate funds have investment minimums of $5,000 or less.
However, you’ll likely need more than $5,000 to buy a rental property or invest in a house to fix and flip due to all the upfront costs of acquiring a property (down payment and real estate closing costs) and expenses to renovate the property or hold it until you rent it out.
How can I begin investing in real estate?
The easiest way to begin investing in real estate is to buy shares of a REIT or real estate fund. You can get started for only $10 in some cases (Fundrise has a $10 minimum investment). You can steadily invest more as you have additional money to invest to grow your real estate portfolio.
What is the 2% rule in real estate?
The 2% rule in real estate is a popular guideline for determining whether a rental property would make a good investment. The rule states that the property should generate monthly rental revenue of at least 2% of the purchase price. For example, if you are considering a rental property that costs $250,000 to buy, it should generate at least $5,000 in rental income each month.



